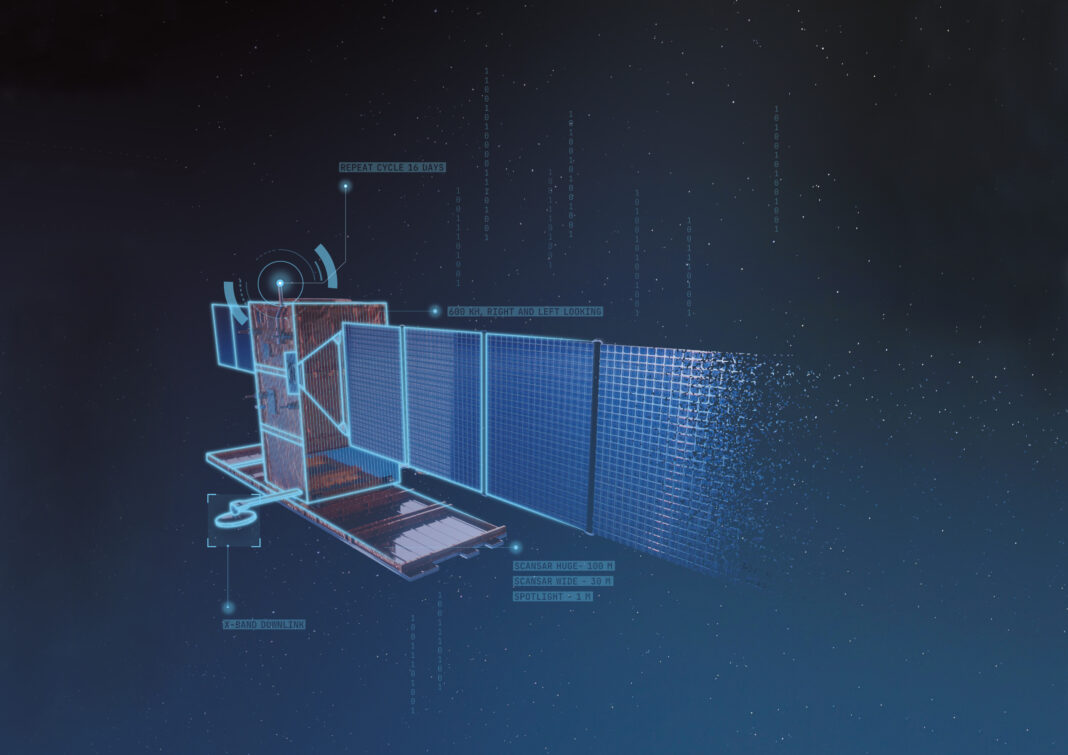
Supercomputers, artificial intelligence, and cloud are aboard a constellation of cyber-secure satellites orbiting the Earth this is the objective of the «Military Space Cloud Architecture» (MILSCA) study project assigned to Leonardo by the Italian Ministry of Defense (through the contractual agency Teledife), as part of the National Military Research Plan (PNRM).
For the first time in Europe, similar to what happens with the terrestrial cloud, the project intends to define a space architecture capable of providing government and national Armed Forces with high-performance computing and storage capacity directly in space.
According to Leonardo’s press release, this system is designed with integrated cybersecurity models, which will guarantee greater speed and flexibility in the processing and exchange of information. Space Cloud, which will be tested by creating a digital twin of the architecture, will be able to store more than 100 terabytes of data generated on Earth and in space on board each satellite in the constellation. It will be able to perform processing with a power exceeding 250 TFLOPS (250 billion operations per second) with single precision, adopting advanced algorithms using artificial intelligence, machine learning techniques and extensive data analysis. They will also be able to communicate and exchange data autonomously with other satellites.
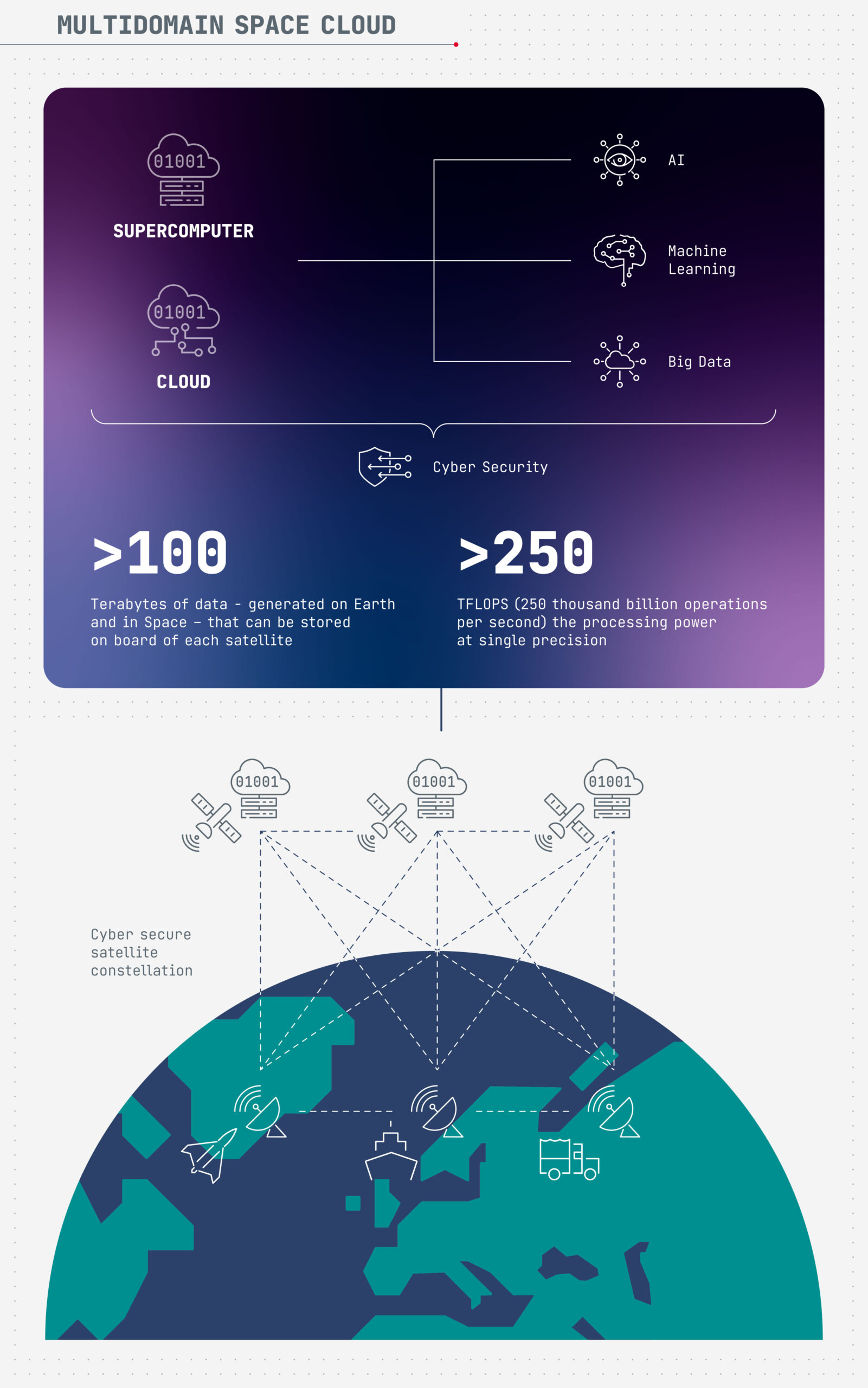
A cyber-secure supercomputer and archive system in space will guarantee users access to strategic data such as communication, earth observation, and navigation data, anywhere, even in the most remote places, and at any time. Furthermore, a Space Cloud system significantly reduces data processing times, which is processed directly in orbit, providing real-time information, and thus facilitating multi-domain and multi-nation operations. The transmission networks will be left free for other connections thanks to the only transfer of information of interest to Earth. In addition, storing data in orbit will also represent a useful back-up of the Earth centers, which are most exposed to natural disasters.
The project has Leonardo as leader with the participation of the joint ventures Telespazio (67% Leonardo, 33% Thales) and Thales Alenia Space (67% Thales, 33% Leonardo). With a duration of 24 months, the study includes a first phase of architecture definition and a second phase that will conclude with the development of a digital twin of the satellite using HPC (High Performance Computing) and the multi-constellation satellite terminal demonstrator. The objective is to simulate different application scenarios in a digital environment. These tests will be carried out thanks to Leonardo’s supercomputer, the davinci-1, one of the world’s first aerospace and defense HPCs in terms of computing power and performance. The study will be a precursor to another experimental phase which, if confirmed, will involve the deployment in orbit of a demonstration constellation of satellites.