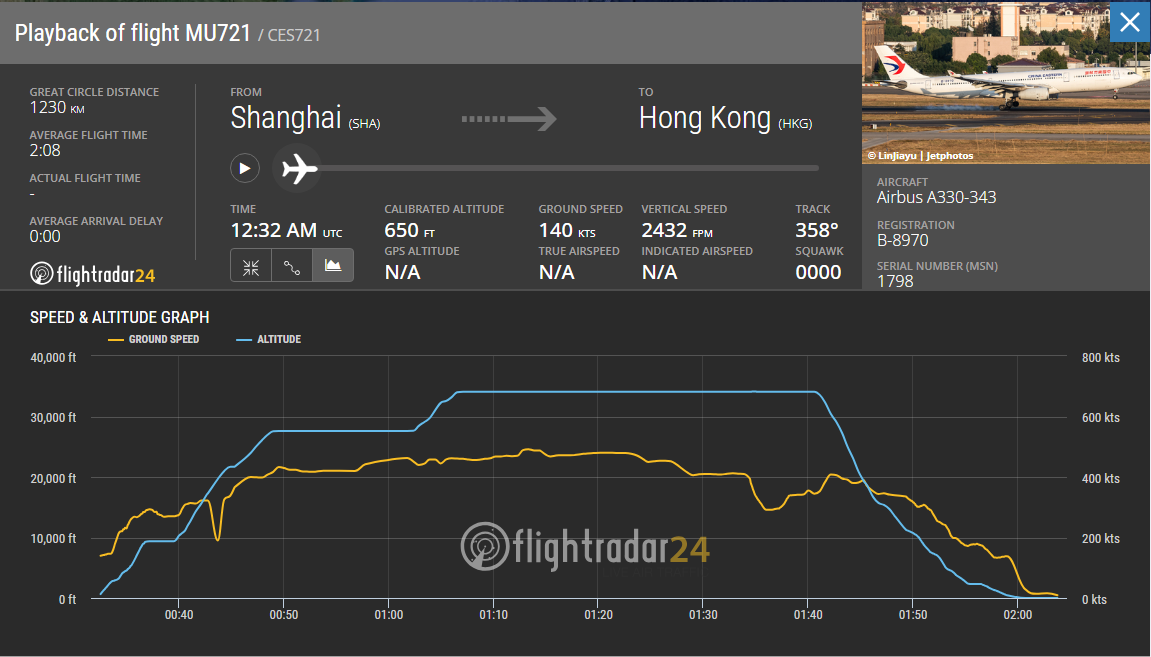
On Sunday, December 3, a China Eastern Airbus A330-300 operating flight MU721 from Shanghai to Hong Kong had to declare an emergency due to an uncontained engine failure.
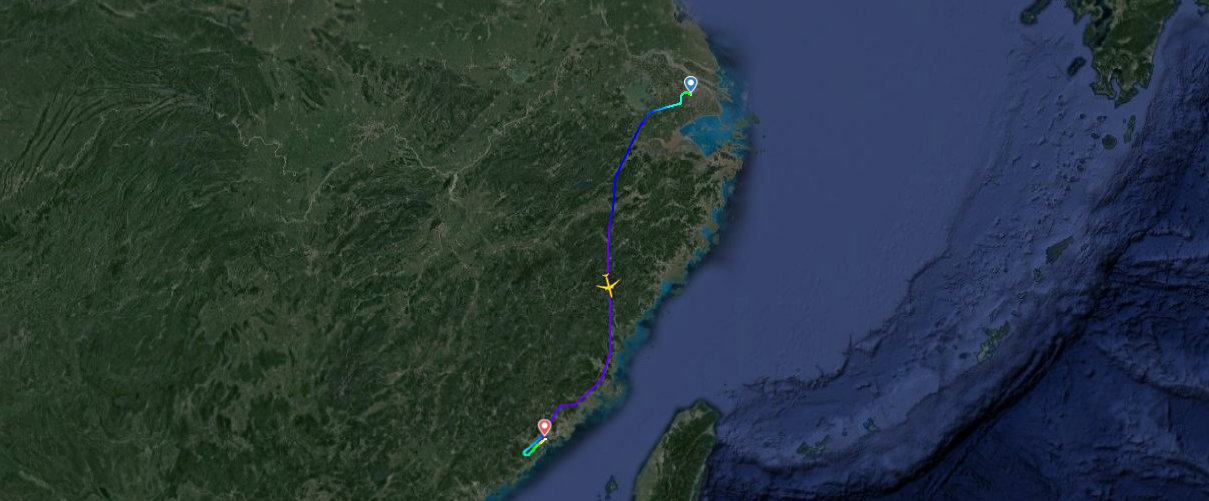
The aircraft, an Airbus A330-343 with registration B-8970, was delivered to China Eastern in June 2017 and is equipped with two Rolls-Royce Trent 772B/C-60 engines. It took off from Shanghai at 8:32 am local time and flew for approximately an hour and a half before diverting and landing at 10:50 am at Xiamen airport, 1000 kilometers from the origin airport and only 460 kilometers from its scheduled destination, Hong Kong.
China Eastern MU721 /Aiburs A330 diverted due to uncontained engine failure. pic.twitter.com/NdAFFwk6su
— ChinaAviationReview (@ChinaAvReview) December 3, 2023
What is an uncontained engine failure?
An uncontained engine failure is a serious type of incident where components of the engine break and are ejected outside the engine casing. Unlike a contained failure, where any broken parts are retained within the engine structure or expelled through a designated path, an uncontained failure poses a significant risk as fragments can penetrate the aircraft’s fuselage or wing, damaging critical systems or injuring passengers.
This type of failure often results from the disintegration of rotating parts within the engine, such as blades or turbine disks, which can be caused by manufacturing defects, fatigue, or foreign object damage. The high-speed rotation of these components means that, when they break, they are ejected with great force, leading to catastrophic consequences.
There have been notable incidents of uncontained engine failures in aviation history. One example is the United Airlines Flight 232 incident in 1989, where a fan disk failure in the tail engine led to a loss of hydraulic control of the aircraft, resulting in an emergency landing.
In February 2018, Southwest Airlines Flight 1380 experienced an uncontained failure when a blade broke off from the engine, causing debris to damage the fuselage and a passenger window, leading to depressurization and the death of a passenger.






